A stroke is caused when the blood supply to the brain is reduced or blocked, usually because a blood vessel in the brain is ruptured or blocked by a clot.
- Types of Stroke
- Signs and Symptoms
- Risk Factors
- How is stroke diagnosed?
- Preventive measures
There are 2 main types of stroke
Ischemic stroke
- Ischemic stroke
- Transient ischemic stroke (TIA or mini-stroke)
Hemorrhagic stroke
Ischemic Stroke (Clot)
Ischemic stroke occurs when the brain does not receive enough blood due to blockage in the blood vessel carrying blood to the brain.
Ischemic stroke: TIA (Transient ischemic attack)
TIA is also known as “mini stroke”. It is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. The symptoms of TIA last for about 1 to 5 minutes. It does not cause permanent damage or disability but can lead to full blown stroke if untreated.
Hemorrhagic Stroke (Bleed)
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when weak vessels in the brain are ruptured and bleed into the brain causing compression of the surrounding brain tissues.
Symptoms of a stroke depend on which part of the brain is injured and how severely it is affected. A very severe stroke can cause sudden death. (WHO)
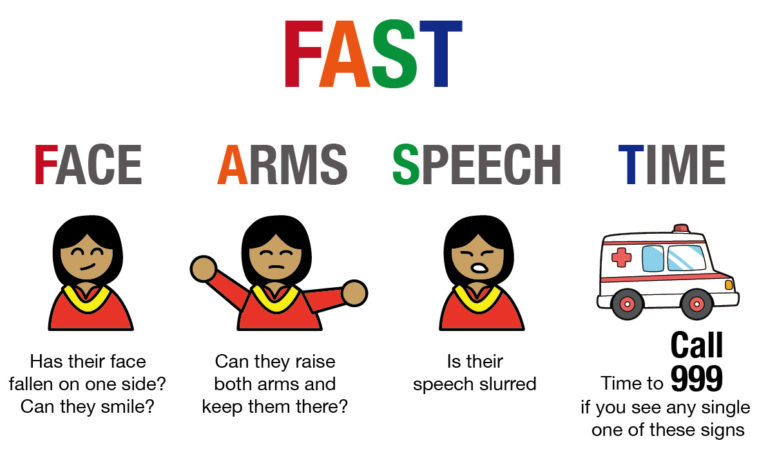
FAST is an easy way to remember and identify most common stroke signs and symptoms.
Lack of physical activity

- Age
- Family medical history
- Gender
- Previous TIA or stroke
Unhealthy diet


Smoking
Excessive alcohol intake
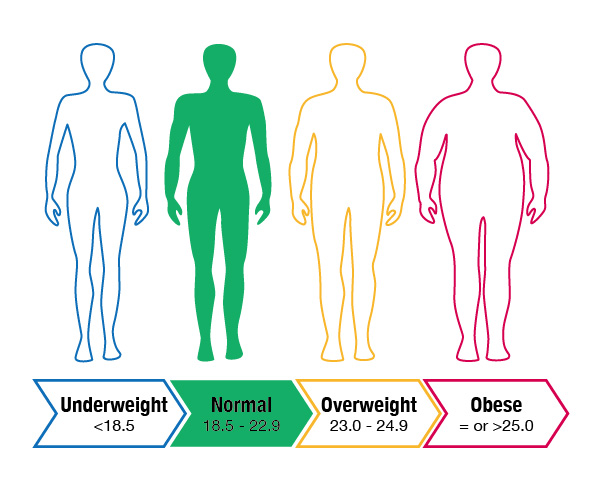
Being obese

Medical history: The following medical conditions increase your risk of having stroke
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Carotid artery disease: Blockage of the neck arteries
- Atrial fibrillation: Irregular heartbeat that can lead to blood clots and stroke.
- Other heart diseases: Several other heart conditions such as, heart failure, and heart valves diseases increase your risk of having stroke.
- CT scan: CT scan produces a large image of the brain to show the exact reason, type and location of stroke.
- MRI scan: MRI scan produces a similar image as CT scan but sharper and more detailed. It shows the extent and location of much smaller injuries in the brain.
- Ultrasound: : Ultrasound machine is used on the neck vessels that supply blood to the brain to determine the flow of the blood in the vessels. It shows if there is any blockage due to fat deposition (clots) in any of the neck vessels.
- Angiography: It gives a picture of the blood flowing through the vessels on the computer screen.
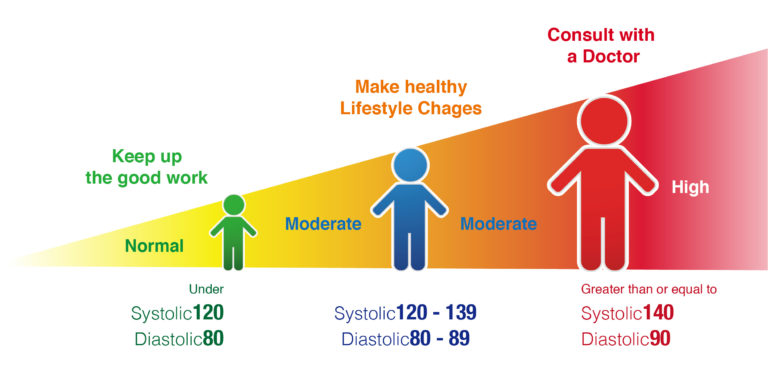
Tight control of blood pressure
Reduce salt and fat intake in your diet
Eat more fruits and vegetables every day

Do regular exercise (30 min every day)

Have meals rich in whole grains
Stop Smoking

Maintain a healthy body weight
Avoid excessive use of alcohol