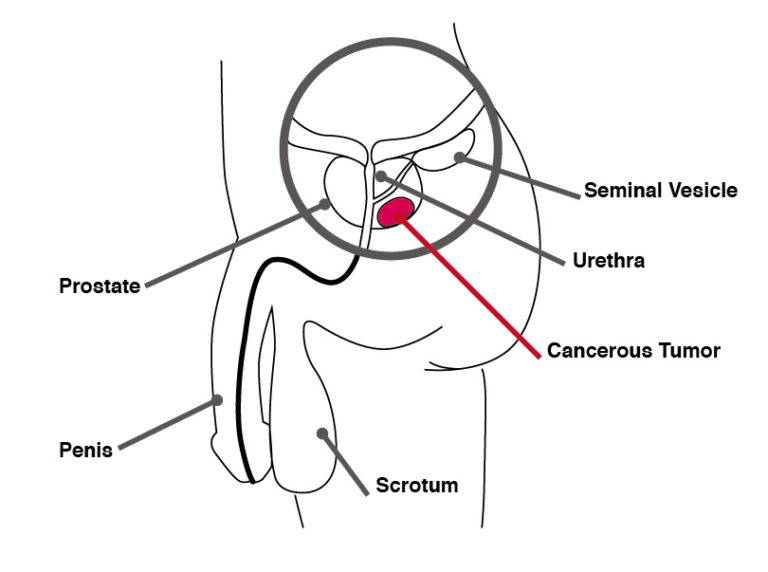
Prostate cancer develops when cells in the prostate start to grow in an uncontrolled way.
- Prostate is a small gland in the pelvis found only in men.
- It is located between the penis and the bladder and surrounds the urethra.
- Statistics
- Signs and symptoms
- Risk factors
- Screening Tests
- Preventive measures
Hong Kong
Incidence rate: 27.5 per 100,000 populations in males
Mortality rate: 4.3 per 100,000 populations in males
(Hong Kong Cancer Registry, 2020)
Pakistan
Incidence rate: 6.3 per 100,000 populations in males
Mortality rate: 3.0 per 100,000 populations in males
(IARC, 2021)
Nepal
Incidence rate: 3.0 per 100,000 populations
Mortality rate: 1.5 per 100,000 populations
(IARC, 2021)
India
Incidence rate: 5.5 per 100,000 populations
Mortality rate: 2.7 per 100,000 populations
(IARC, 2021)
Indonesia
Incidence rate: 11.6 per 100,000 populations
Mortality rate: 4.5 per 100,000 populations
(IARC, 2021)
Prostate cancer and prostate enlargement has similar urinary symptoms.
- Difficulty or delay in urinating
- Slow or weak stream of urine
- Blood in urine
- Pain in the lower back and hips
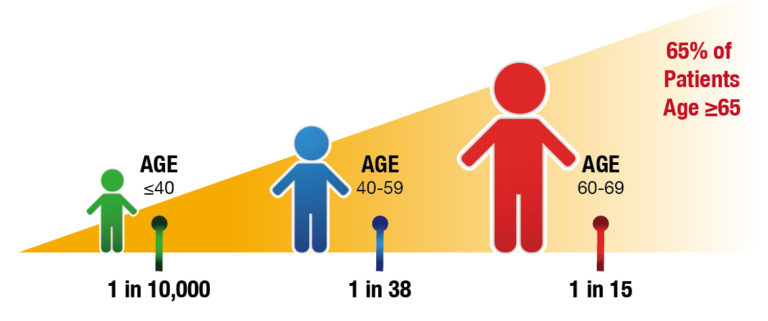
Age: Risk increases with age
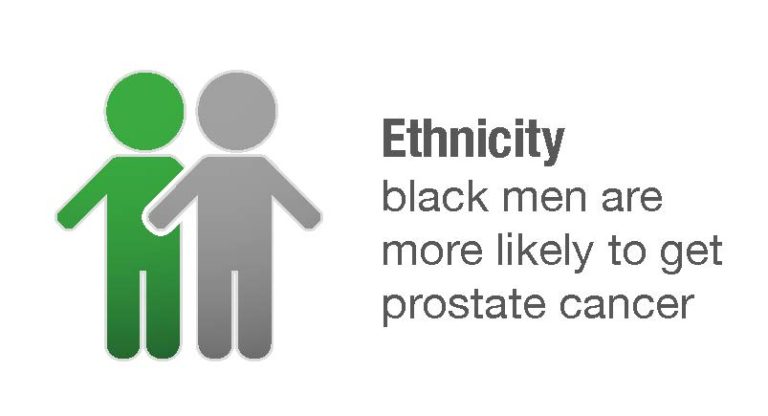
Race/ethnicity
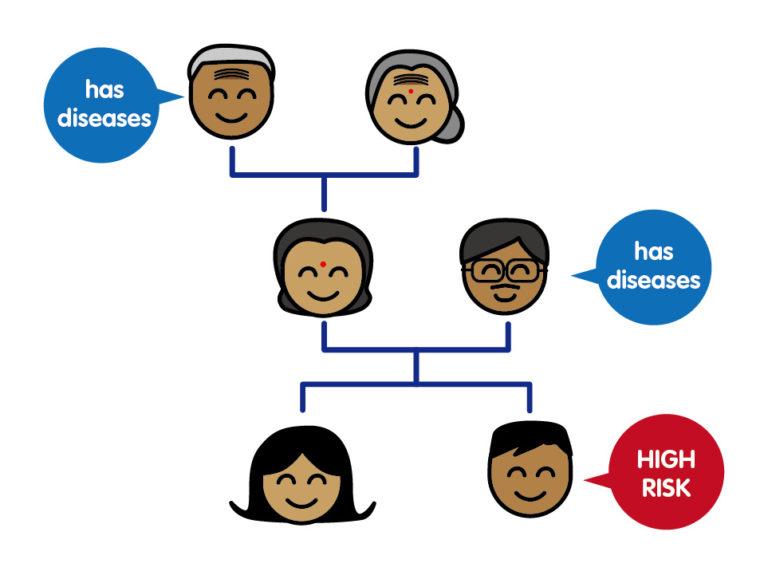
Family medical history
- If your parent, sibling, or children has prostate cancer, you are at a higher risk of developing the disease.
Two main tests are performed for prostate cancer screening
- Digital rectal exam (DRE): The doctor or nurse inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the prostate to check for anything abnormal.
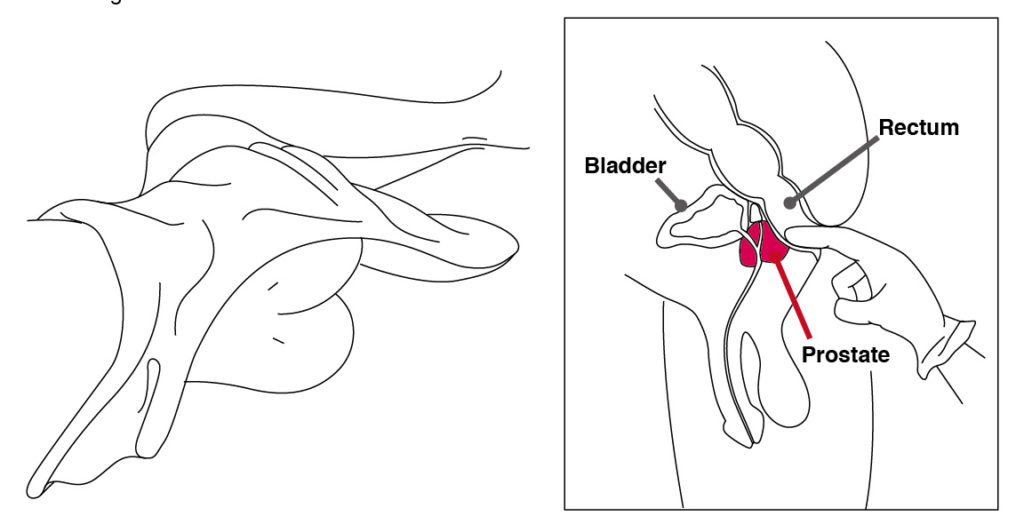
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: PSA test is performed to check the level of PSA in the blood.
Department of Health (2017). Prostate cancer prevention and screening. Retrieved at:https://www.chp.gov.hk/files/pdf/5_prostate_cancer_prevention_and_screening_eng.pdf
Eat more vegetables and fruits

Do regular exercise (30 minutes every day)

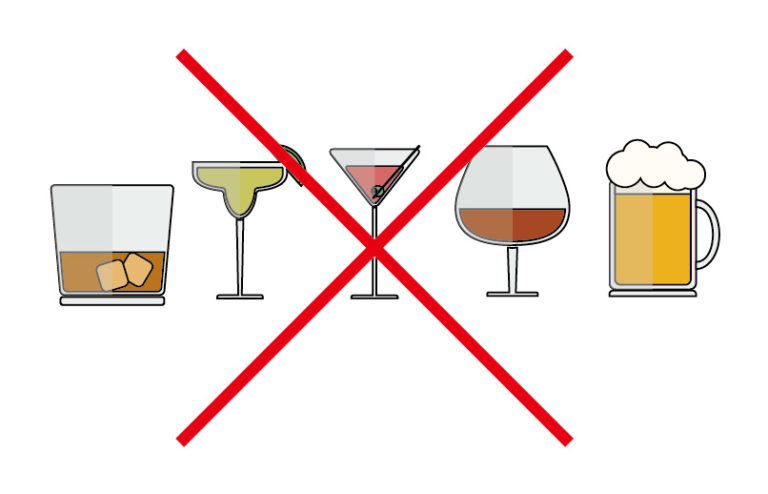
Reduce alcohol intake
Do not smoke

Maintain a healthy body weight